Alberta deputy premier says sovereignty act not a power grab, eyes changes to bill
Alberta's deputy premier says amendments may be needed to clear up confusion over a bill that grants Premier Danielle Smith and her cabinet unfettered power outside the legislature to rewrite laws and direct agencies to resist federal rules.
“We will consider amendment(s) to Bill 1 to clarify this to avoid confusion,” said Kaycee Madu in a series of Twitter posts on Wednesday and Thursday.
Madu said his reading of the bill indicates that cabinet does not have such power and all unilateral cabinet decisions would still have to go back to the legislature for approval.
“It then goes through the normal cabinet process and ultimately a bill will be tabled,” wrote Madu, who is a lawyer and Alberta's former justice minister.
However, the bill does not state that cabinet decisions made under the act would have to go back to the house.
Madu's office did not return a request for comment or explanation about whether amendments are coming. Smith's other deputy premier, Nathan Neudorf, has said he, too, believes legislative safeguards are in place but he hasn't read the eight-page bill.
Justice Minister Tyler Shandro, who is helping Smith shepherd the bill through the house, told reporters he wasn't aware of Madu's comments. He said the United Conservative Party government is listening to reaction and concerns.
“We're hearing the feedback on opportunities to make (the bill) more clear,” said Shandro. “No decisions have been made (on amendments).”
The bill, titled the Alberta Sovereignty Within a United Canada Act, was introduced Tuesday by Smith.
Smith has described it as a deliberately confrontational tool to reset the relationship with a federal government she accuses of interfering in constitutionally protected areas of provincial responsibility from energy development to health care.
Political scientists, the Opposition NDP and constitutional experts say the bill grants sweeping powers to cabinet that are normally reserved for extreme circumstances, like natural disasters, that require swift legislative action.
Those changes, they say, make it dangerous to democracy.
Under the bill, cabinet would decide when Ottawa is interfering in Alberta jurisdiction through a law, policy or program or through a looming federal initiative it believes may cause harm.
Cabinet would send a resolution to the legislative assembly spelling out the nature of the harm and the remedies to fix it.
If the legislature gives its approval, that is where its involvement ends and cabinet takes over.
The bill grants cabinet powers to unilaterally rewrite laws without sending them back to the legislature for debate or approval. Cabinet would be allowed to direct public agencies, including police, municipalities, school boards, post-secondary institutions and health regions to flout federal laws.
The bill gives cabinet wide latitude on how to interpret the resolution it receives from the assembly. It says cabinet “should” follow the direction of the house, but doesn't mandate it. Instead, cabinet is told to exercise its new extraordinary powers however it deems “necessary or advisable.”
Smith and other members of her front bench are in lockstep on saying the bill stipulates direct legislative oversight over cabinet's actions.
She repeated it in the house Thursday.
Smith also accused the Opposition NDP of “fear-mongering” that “somehow this act gives power to cabinet to unilaterally alter legislation behind closed doors, despite the fact that it does not.”
NDP Leader Rachel Notley responded, “We have heard from no less than seven different legal experts, public servants and constitutional lawyers, who confirm a simple truth: this bill gives the premier the so-called Henry VIII power to write laws behind closed doors with zero input from this assembly.”
Law professor Martin Olszynski, who has written extensively on Smith's bill since she first proposed it in the spring, said it clearly gives cabinet unfettered power to rewrite laws. He asked why, if the bill respects the existing legislative process, as Madu contends, is it needed at all?
“On its face, this is absurd,” Olszynski, with the University of Calgary, said in an interview.
Constitutional law professor Eric Adams at the University of Alberta agreed that what Madu said doesn't square with the text of the bill.
“I can't see anything in Section 4 (of the bill) that says the cabinet is required to table an amendment and subject it to the normal legislative process,” said Adams.
“Section 4 would seem to say the opposite.
“I'm confused by the government's suggestions otherwise.”
Smith has delivered a mixed message on how the bill would ultimately be used.
On Tuesday, her office sent documentation to reporters saying the government hopes to use it in the spring, but that same day she told a news conference it's a last-resort bill and she hopes to never use it.
Indigenous leaders have criticized the bill as heavy-handed and divisive. Business groups, including the Calgary Chamber of Commerce, warn that its legal uncertainty is not good for business and investment.
This report by The Canadian Press was first published Dec. 1, 2022.
CTVNews.ca Top Stories

Widow looking for answers after Quebec man dies in Texas Ironman competition
The widow of a Quebec man who died competing in an Ironman competition is looking for answers.
Tom Mulcair: Park littered with trash after 'pilot project' is perfect symbol of Trudeau governance
Former NDP leader Tom Mulcair says that what's happening now in a trash-littered federal park in Quebec is a perfect metaphor for how the Trudeau government runs things.
World seeing near breakdown of international law amid wars in Gaza and Ukraine, Amnesty says
The world is seeing a near breakdown of international law amid flagrant rule-breaking in Gaza and Ukraine, multiplying armed conflicts, the rise of authoritarianism and huge rights violations in Sudan, Ethiopia and Myanmar, Amnesty International warned Wednesday as it published its annual report.
Photographer alleges he was forced to watch Megan Thee Stallion have sex and was unfairly fired
A photographer who worked for Megan Thee Stallion said in a lawsuit filed Tuesday that he was forced to watch her have sex, was unfairly fired soon after and was abused as her employee.
Amid concerns over 'collateral damage' Trudeau, Freeland defend capital gains tax change
Facing pushback from physicians and businesspeople over the coming increase to the capital gains inclusion rate, Prime Minister Justin Trudeau and his deputy Chrystia Freeland are standing by their plan to target Canada's highest earners.
U.S. Senate passes bill forcing TikTok's parent company to sell or face ban, sends to Biden for signature
The Senate passed legislation Tuesday that would force TikTok's China-based parent company to sell the social media platform under the threat of a ban, a contentious move by U.S. lawmakers that's expected to face legal challenges.
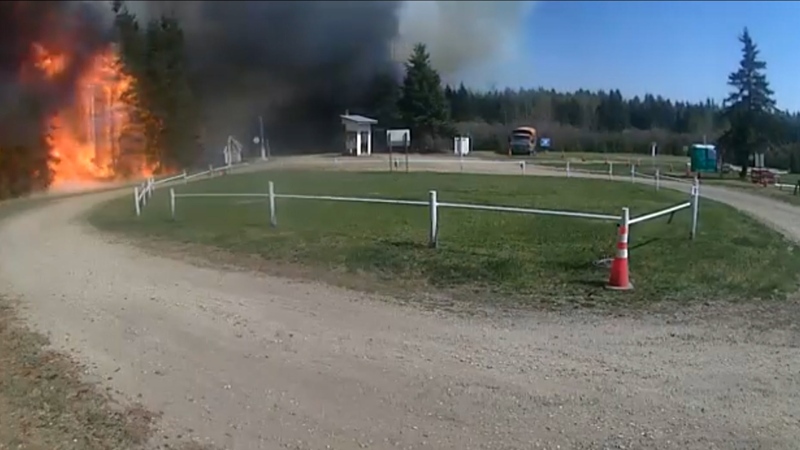
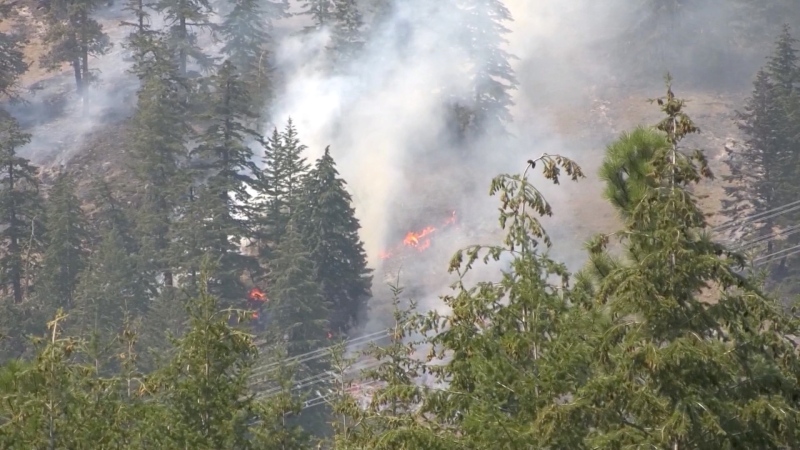
Wildfire southwest of Peace River spurs evacuation order
People living near a wildfire burning about 15 kilometres southwest of Peace River are being told to evacuate their homes.
U.S. Senate overwhelmingly passes aid for Ukraine, Israel and Taiwan with big bipartisan vote
The U.S. Senate has passed US$95 billion in war aid to Ukraine, Israel and Taiwan, sending the legislation to President Joe Biden after months of delays and contentious debate over how involved the United States should be in foreign wars.
'My stomach dropped': Winnipeg man speaks out after being criminally harassed following single online date
A Winnipeg man said a single date gone wrong led to years of criminal harassment, false arrests, stress and depression.