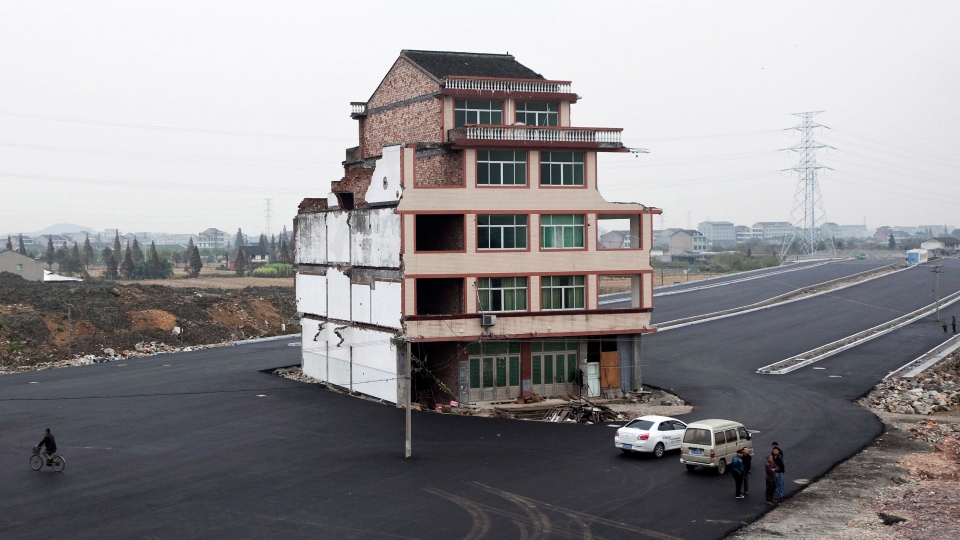
BEIJING -- Authorities have demolished a five-storey home that stood incongruously in the middle of a new main road and had become the latest symbol of resistance by Chinese homeowners against officials accused of offering unfair compensation.
Xiayangzhang village chief Chen Xuecai told The Associated Press the house was bulldozed Saturday after its owners, duck farmer Luo Baogen and his wife, agreed to accept compensation of 260,000 yuan ($41,000).
There was no immediate confirmation from Luo, whose cellphone was turned off Saturday.
The couple had been the lone holdouts from a neighbourhood that was demolished to make way for the main thoroughfare heading to a newly built railway station on the outskirts of the city of Wenling in Zhejiang province.
The razing comes a week after images of the house circulated widely online in China, triggering a flurry of domestic and foreign media reports about the latest "nail house," as buildings that remain standing as their owners resist development are called.
Luo, 67, had just completed his house at a cost of about 600,000 yuan ($95,000) when the government approached him with their standard offer of 220,000 ($35,000) to move out -- which he refused, Chen has previously said. The offer then went up to 260,000 yuan ($41,000) last week.
It was not immediately clear why Luo accepted the compensation in a meeting with officials Friday afternoon when the amount of money offered was the same as a week ago.
Village chief Chen said Luo was tired of all the media attention and voluntarily consented to the deal. "Luo Baogen received dozens of people from the media every day and his house stands in the centre of the road. So he decided to demolish the house," Chen said.
Authorities commonly pressure residents to agree to make way for development with sometimes extreme measures, such as cutting off utilities or moving in to demolish when residents are out for the day. In Luo's case, however, he had told local reporters last week his electricity and water were still flowing.
Real estate is one of the big drivers of China's runaway growth in recent decades. But the rapid development has run into objections from many of the hundreds of thousands of residents who have been forced out to make way for new housing, factories and other business ventures, creating a major source of unrest.